Table of Contents
Properties of Cement:
- Cement is popular binding material due to its properties.
- There are many tests including physical and lab test for testing out different properties of cement.
- Properties of cement can be divided into,
- Physical properties
- Chemical properties
- Properties of cement can be divided into,
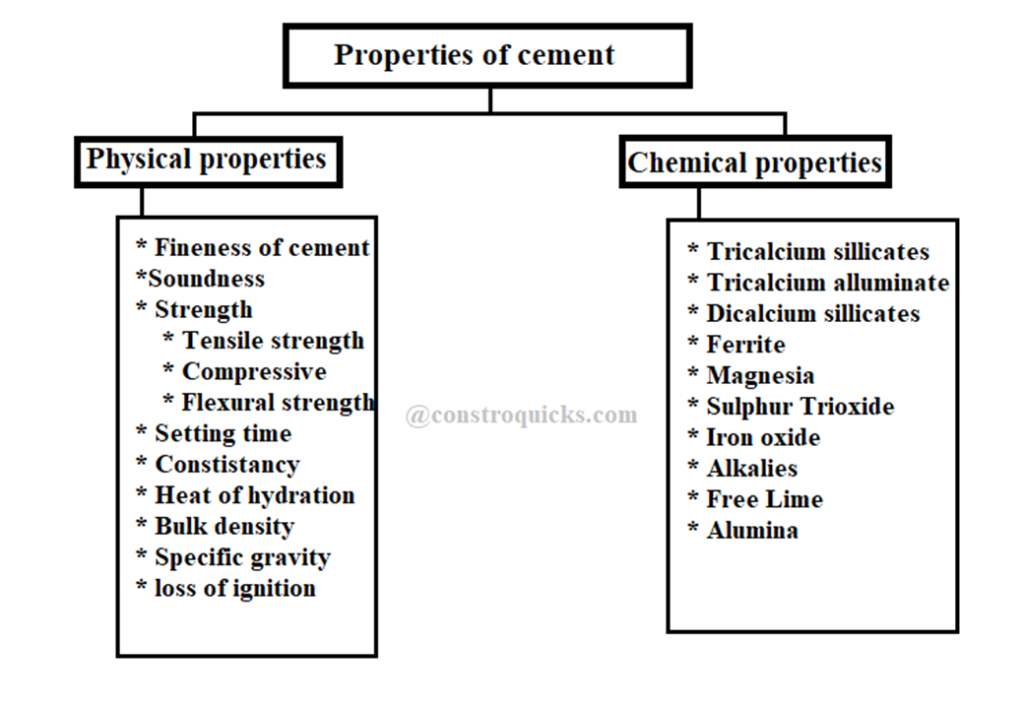
A. Physical Properties of Cement:
- Physical properties of cement are characterized by the structure, composition and physical parameters of cement.
- All of the physical properties are very much important parameters to control the quality of cement while production as well as casting on construction site.
- Some of the physical parameters are listed below,
- Fineness of cement
- Soundness
- Consistency
- Strength
- Setting time
- Heat of hydration
- Loss of ignition
- Bulk density
- Specific gravity (Relative density)
Fineness of Cement
- The particle size of cement is very much important parameter and responsible for bond and strength of cement.
- More will be the surface area of cement particle; more will be the strength of cement.
- The test to find out Fineness of cement is also termed as Fineness test for cement.
Soundness of Cement
- Here the soundness of cement referred as expansion or shrinkage of cement after hardening.
- Both expansion and shrinkage of cement can be harmful for construction and can reduce the strength of cement and bondage also.
- The tests to find out soundness of cement is Le Chatelier test and Autoclave Test.
Consistency of Cement
- The consistency of cement is nothing but working with cement paste with ease.
- Or in other words, consistency also defined as the ability of cement paste to flow and work with easily.
- Consistency of cement can be measured by Vicat test.
Strength of Cement
- There are three types of strengths of cement are measured, Compressive strength, tensile strength and Flexural strength.
- Compressive strength:
- In this test the resistance of cement against the compressive load will be tested and this strength is termed as compressive strength.
- Tests to measure the compressive strength: Compressive Cube test
- Tensile strength:
- In this test the resistance of cement against the tensile load will be tested and this strength is termed as Tensile strength.
- Tests to measure the tensile strength: Tensile test
- Flexural strength:
- In this test the resistance of cement against the flexural load will be tested and this strength is termed as flexural strength.
- Tests to measure the Flexural strength: Flexural test
Setting Time of Cement
- Setting time of cement is termed as time required for cement to set.
- Setting time is also has two types,
- Initial setting time: Time required for cement paste to gets a rigidity. (Generally, varies from 30-45 minutes)
- Final setting time: time required for cement paste to completely gets harden. (Generally, varies up to 10 hours)
- Standard Tests to measure setting time:
- Time of Setting of Hydraulic Cement by Vicat Needle
- Time of Setting of Hydraulic Cement by Gillmore Needles
- Time of Setting of Hydraulic-Cement Paste by Gillmore Needles
Heat of Hydration
- When water is added into the cement the reaction is takes place which generates heat and this process of formation heat is known as heat of hydration.
- Heat of hydration is important parameter in term of bond, curing and strength of cement.
- Standard Test: Heat of Hydration of Hydraulic Cement
Loss of Ignition
- Heating up the cement sample up to 900 – 1000°C cause weight loss in cement sample due to heating, this loss of weight is termed as loss of Ignition of cement.
- Standard Test: Chemical Analysis of Hydraulic Cement
Bulk density
When cement is mixed with water, the water replaces areas where there would normally be air. Because of that, the bulk density of cement is not very important.
Cement has a varying range of density depending on the cement composition percentage.
The density of cement may be anywhere from 62 to 78 pounds per cubic foot.
Specific Gravity (Relative Density)
Specific gravity pf cement is important parameter while calculating the cement quantity for the concrete.
Generally, for Portland cement specific gravity is 3.15.
Test to measure the specific gravity: Density of cement
B. Chemical Properties of Cement:
- Chemical properties of cement is properties comes by the basic raw materials of cement.
- Cement is generally made up of limestone, sand, clay, aluminium, iron ores and can be included chalk, shale, clay, various slags, slate, marl.
- Following are the some of the chemical properties of cement
- Tricalcium aluminate (C3A)
- Tricalcium silicate (C3S)
- Dicalcium silicate (C2S)
- Ferrite (C4AF)
- Magnesia (MgO)
- Sulphur trioxide
- Iron oxide/ Ferric oxide
- Alkalis
- Free lime
- Silica fumes
- Alumina
- Tricalcium aluminate (C3A), Tricalcium silicate (C3S), Dicalcium silicate (C2S) and Ferrite (C4AF) are also known as Bogues compound and mainly responsible for strength and setting time of cement.
- Tricalcium aluminate (C3A): make cement sulfate resistant and responsible for strength of cement.
- Tricalcium silicate (C3S): Responsible for early strength and initial setting of cement also imparts rapid hydration.
- Dicalcium silicate (C2S): Responsible for early strength
- Ferrite (C4AF): Responsible for rapid hydration and does nt imparts any strength in cement.
- Magnesia (MgO): It makes cement unsound and expensive. It also can add strength to the cement.
- Sulphur trioxide: Sulphur trioxide in excess amount can make cement unsound.
- Iron oxide/ Ferric oxide: Iron oxide or ferric oxide is mainly responsible for the color of the cement.
- Alkalis: Can produce difficulties in setting time of cement.
- Free lime: Free lime cement can cause expansion in cement.
- Silica fumes: Imparts high strength to the cement.
- Alumina: Responsible for quick setting time.